National and local governments sometimes implement price controls legal minimum or maximum prices for specific goods or services to attempt managing the economy by direct intervention price controls can be price ceilings or price floors.
Define price ceilings and price floors and provide examples.
Which leads to a surplus.
A price ceiling is the legal maximum price for a good or service while a price floor is the legal minimum price.
Basically the purpose of the price ceiling is to make prohibition for the people who charge high prices from their customers and this protect and prevent them.
It has been found that higher price ceilings are ineffective.
Price ceiling has been found to be of great importance in the house rent market.
Price ceiling is one of the approaches used by the government and the purpose of which is to control the prices and to set a limit for charging high prices for a product.
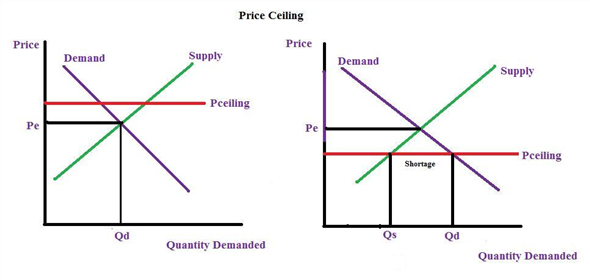
If the government sets a price ceiling of 15 per unit for this good the quantity demanded will be 3 500 units whereas the quantity supply will be 1 500 units.
Real life example of a price ceiling in the 1970s the u s.
Which leads to a shortage.
For example labor costs in the united states have a price floor of.
What is the purpose of setting a price floor and price ceiling.
Price ceiling is a situation when the price charged is more than or less than the equilibrium price determined by market forces of demand and supply.
In this case there is a supply shortage equal to 2 000 units for this particular product.
As a result shortages quickly developed.
From a financial perspective price ceilings can often send mixed messages to.
Price floor is a price control typically set by the government that limits the minimum price a company is allows to charge for a product or service its aim is to increase companies interest in manufacturing the product and increase the overall supply in the market place.
They can also force sellers to create unregulated black markets and high priced required add ons.
Price ceilings on gasoline by the u s.
Price ceilings also don t work if the natural market clearing price is below the ceiling for example a 75 000 price ceiling for cars when most cars sell for 20 000.
Another example of a price ceiling involved the coulter law regarding the vfl in australia.
This control may be higher or lower than the equilibrium price that the market determines for demand and supply.
Government in the 1970s made gasoline more affordable to consumers.
However it resulted in a shortage due to increased demand.
When price floors are set it means that the government imposes a minimum price for a product.
Solution for define price ceiling and price floor and give an example of each.